解析 Webpack Bundle 的程式碼
Webpack 做為管理模組化 JavaScript 的工具,最後會將所有的模組編譯為一隻 JavaScript 檔案(bundle),讓所有模組可以在瀏覽器上執行。
拆解 Bundle 檔能夠更暸解 Webpack 的運作,它如何載入模組,並兼容既有的模組系統,
這篇文章出現的程式碼都可以在 compare-webpack-bundle 找到
大綱:
- 基本 Webpack 設定
- Bundle 結構
- __webpack_require__
- CommonJS 模組
- ES2015 模組
- ES2015 模組載入 CommonJS
- CommonJS 載入 ES2015
基本 Webpack 設定
從最基本的 Webpack 設定,產出一個乾淨的 bundle 檔,是研究 bundle 檔很好的開始。
一個基本的 Webpack 設定,只需要包含 Entry(模組進入點) 以及 Output(bundle 檔產出位置) 兩個選項。
檔案結構:
├─ (bundle.js) # 即將產出的 bundle 檔
├─ index.js # entry 模組進入點
└─ webpack.config.js # webpack 設定檔
webpack.config.js:
const path = require('path')
module.exports = {
entry: path.resolve(__dirname, 'index.js'),
output: {
filename: 'bundle.js',
path: __dirname
}
}
Bundle 結構
webpack 執行剛剛的設定會產生如下的 bundle 檔
/******/ (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var installedModules = {};
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
/******/ return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
/******/ }
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
/******/ i: moduleId,
/******/ l: false,
/******/ exports: {}
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
/******/
/******/ // Flag the module as loaded
/******/ module.l = true;
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports;
/******/ }
/******/
/******/
/******/ // expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
/******/ __webpack_require__.m = modules;
/******/
/******/ // expose the module cache
/******/ __webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/******/
/******/ // define getter function for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = function(exports, name, getter) {
/******/ if(!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, name, {
/******/ configurable: false,
/******/ enumerable: true,
/******/ get: getter
/******/ });
/******/ }
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
/******/ __webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
/******/ var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
/******/ function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
/******/ function getModuleExports() { return module; };
/******/ __webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
/******/ return getter;
/******/ };
/******/
/******/ // Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = function(object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
/******/
/******/ // __webpack_public_path__
/******/ __webpack_require__.p = "";
/******/
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0);
/******/ })
/************************************************************************/
/******/ ([
/* 0 */
/***/ (function(module, exports) {
// This is a blank entry
/***/ })
/******/ ]);
外層是一個 IIFE,將 bundle 獨立執行,內部整個 bundle 的結構可以分成兩個部分(1)載入相關的幫助函式(2)編譯後的模組程式碼
(function(modules) {
// 1. 載入相關的幫助函式
})(
// 2. 編譯後的模組程式碼
[
(function(module, exports) {}),
]
);
載入相關的幫助函式
webpack 在瀏覽器可以有不同的載入方式:
依據載入的方式不同,這部分會增加不同的程式碼,像是「動態載入模組」就增加非同步載入 script 相關的程式碼。
最簡單的載入方式就是同步載入,核心只有一個 __webpack_require__ 函式,負責記錄載入的模組以及執行模組。
除了定義幫助函式,這部分也使用 __webpack_require__ 執行進入點的模組,讓程式可以開始執行。
// 執行進入點
return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = 0);
編譯後的模組程式碼
從進入點下的所有模組(包括所有依賴模組),都會被放在這部分,用一個陣列將所有相關的模組儲存起來。
模組的程式碼經過編譯也會有所改變,跟模組相關的方法或語法(例:import、export 與 require())會被替換。
例如 import xxx from '../modules/xxx' 被替換成 __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__modules_xxx__ = __webpack_require__(1);。
__webpack_require__(1) 的數字 1 就是 xxx 模組在陣列中的位置,下面會再詳細說明。
__webpack_require__
在幫助函式中的 __webpack_require__,是負責執行模組的程式碼,然後取得模組的匯出資訊。
var installedModules = {};
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
// 1. 快取
if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
}
// 2. 創建紀錄模組資訊的物件
var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
i: moduleId,
l: false,
exports: {}
};
// 3. 執行模組
modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
module.l = true;
// 4. 回傳載入的結果
return module.exports;
}
__webpack_require__ 接收參數 moduleId,moduleId 模組的編號。
1. 快取
if(installedModules[moduleId]) {
return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
}
模組只應該被執行一次,installedModules 會儲存已經載入過的模組,如果 installedModules 已經存在就直接回傳。
2. 創建紀錄模組資訊的物件
var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
i: moduleId, // index: 模組的編號
l: false, // loaded: 是否被執行
exports: {} // 模組的匯出物件
};
這邊會將模組的資訊初始化,並塞入快取中。
3. 執行模組
modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__); // 執行模組
module.l = true; // 紀錄模組已經執行過
return module.exports // 回傳 exports 的內容
第一行用 .call 來執行傳進來的模組,讓模組接收到 module, module.exports 與 __webpack_require__ 參數。
module 與 module.exports 在模組執行的過程會被賦予該模組匯出的變數,之後作為 __webpack_require__ 的結果回傳。
總結 __webpack_require__ 的用途就是,執行模組內的程式碼,並將匯出的變數回傳。
CommonJS 模組
之前提到 Webpack 支援多種模組,比較重要的是 ES2015 與 CommonJS,CommonJS 在 Webpack 1 就已經支援,ES2015 則到 Webpack 2 才內建支援。
CommonJS 模組編譯後的程式碼比較簡單,ES2015 看起來則是稍微複雜。
所以先來看一下 CommonJS 的模組:
index.js:
var cjsModule = require('../../modules/cjs-module')
console.log(cjsModule.name)
cjsModule()
modules/cjs-module.js:
var name = 'cjs-module.js'
var cModule = function cModule () {
console.log('This is ' + name + ' with common.js export syntax')
}
cModule.name = name
module.exports = cModule
index.js 是 webpack 的進入點,並載入 cjs-module.js 模組,cjs-module.js 匯出兩個變數,模組預設值 cModule 函式與 name 變數。
編譯後的 index.js:
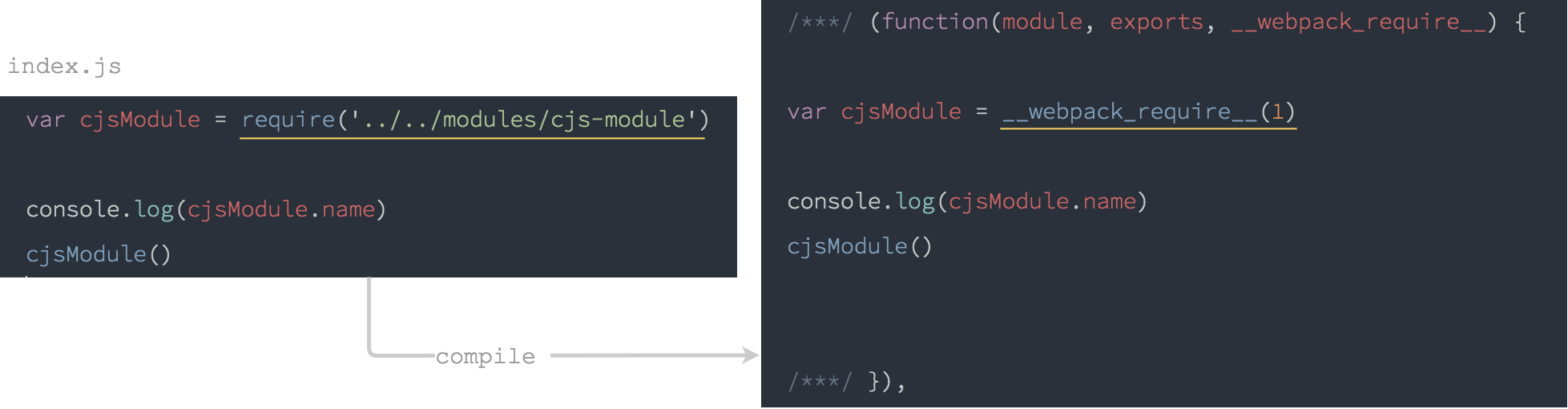
可以發現載入的時候,require 被替換成 __webpack_require__,1 則是 cjs-module 在模組陣列中的編號。
編譯後的 cjs-module.js:
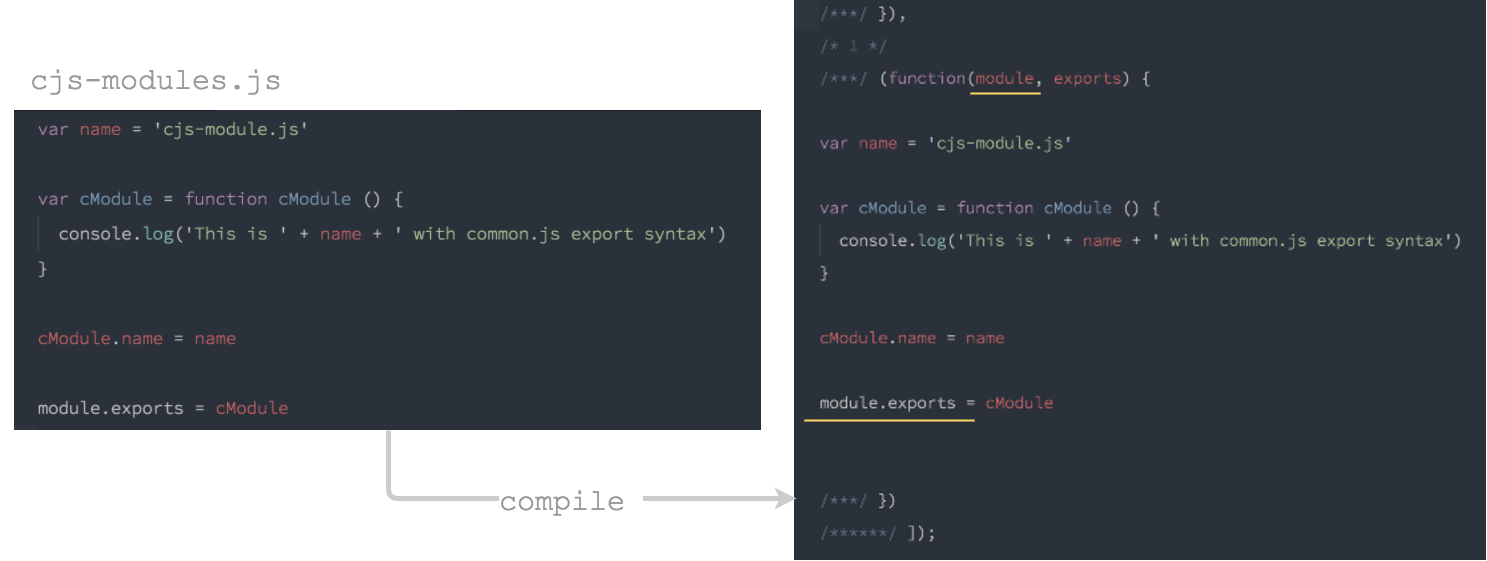
cjs-module.js 被編譯過後完全長一樣,值得注意的是模組中,被傳進來的參數 module 與 export,傳進來的時機是在 __webpack_require__ 執行模組的時候。
參數 module 的屬性 export,與參數 export 的參照實際上是一樣的,CommonJS 規範可以使用 exports 匯出模組,但 module.exports 也被大部分的 CommonJS 實作(ex. Node.js)支援,webpack 也同樣支援兩種方式,所以給兩個參數的用意是,不管使用哪一種方式匯出,程式碼都不用經過轉換。
ES2015 模組
ES2015 轉換後就沒有這麼直觀了,ES2015 的 import 與 export 屬於語法的層面,而不像是 CommonJS 就只是單純在 Object 上賦值。
假設我們有一個進入點 index.js,index.js 會載入 es6-module.js 這個模組。
index.js:
import es6Module, { name } from '../../modules/es6-module'
console.log(name)
es6Module()
es6-module.js:
// Named export
export const name = 'es6-module.js'
// Default export
export default function () {
console.log('This is ' + name + ' with ES6(harmony) export syntax')
}
編譯後的 index.js:
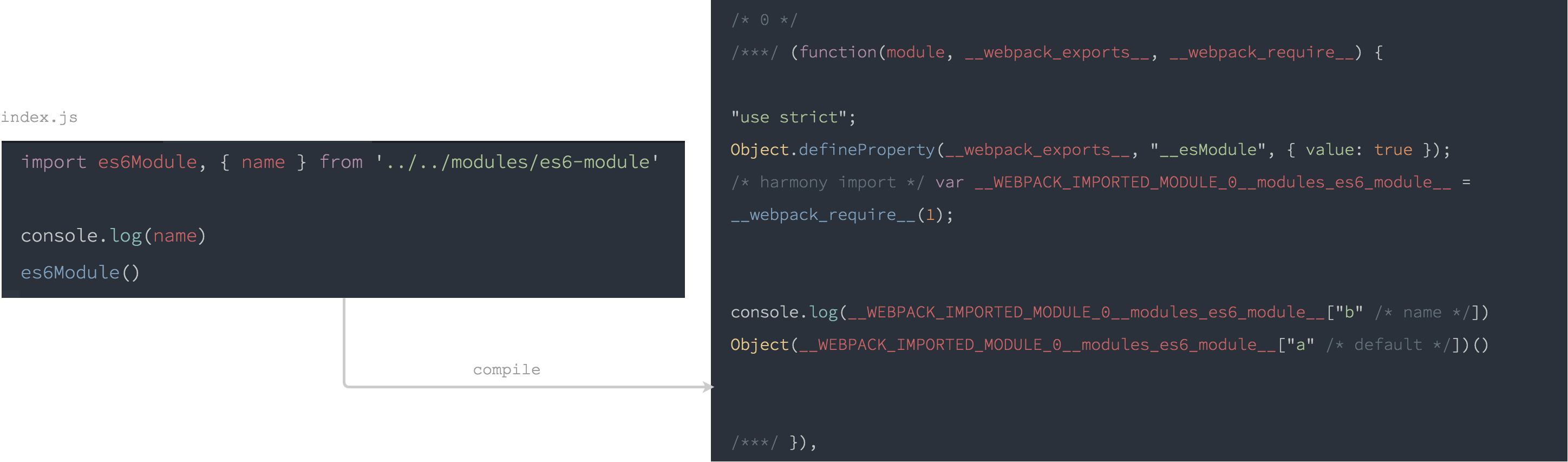
一樣使用 __webpack_require__() 來載入模組 es6-module.js,但是取得 cjs-module 所匯出的變數時,變數 name 用 __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__modules_es6_module__["b"] 代替,預設值則是 __WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__modules_es6_module__["a"]。
"b" 跟 "a" 到底是哪裡來的呢?來看看 es6-module
編譯後的 es6-module.js:
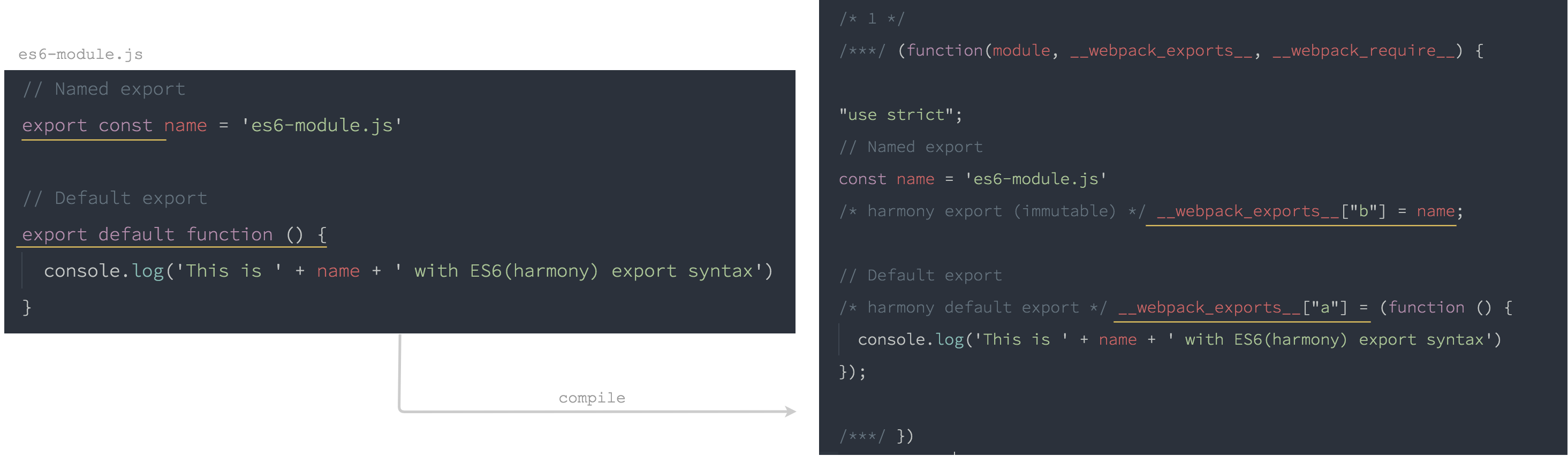
編譯時 export 就已經被替換掉了
export const name替換為__webpack_exports__["b"] = nameexport default替換為__webpack_exports__["a"] =
es2015 的模組在匯出時,會被編譯為能夠賦值到物件上的形式,就如同 CommonJS 一樣,讓模組載入時可以存取匯出的變數。
ES2015 模組載入 CommonJS
分別看過 CommonJS 模組與 ES2015 模組的編譯,那假如是 ES2015 載入 CommonJS 呢?或者,CommonJS 載入 ES2015?
先來看看 ES2015 載入 CommonJS。
進入點 index.js:
import cjsModule from '../../modules/cjs-module'
console.log(cjsModule.name)
cjsModule()
cjs-module.js:
var name = 'cjs-module.js'
function cModule () {
console.log('This is ' + name + ' with common.js export syntax')
}
cModule.name = name
module.exports = cModule
編譯過後的 index.js:
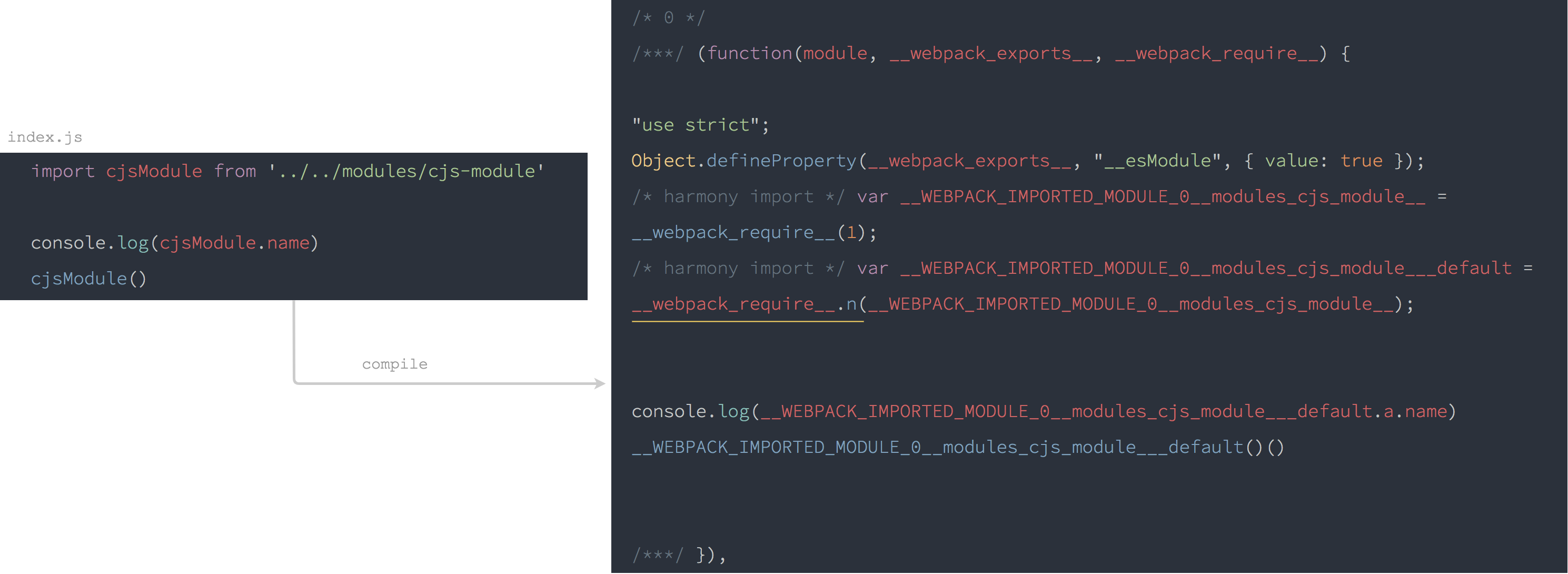
編譯過後的 cjs-module 沒有改變,但是編譯後的 index.js 取得 CommonJS 模組預設值的時候,呼叫了 __webpack_require.n(cjs-module)。
__webpack_require__.n:
__webpack_require__.n = function(module) {
var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
function getModuleExports() { return module; };
__webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
return getter;
};
__webpack_require__.n 的作用是,判斷 __esModule 的屬性是否為 true,true 則代表匯入預設值時,要取用的是在 module.exports.default 上的值。
什麼情況預設值會在 module.exports.default?,在 webpack 中 ES6 模組被轉換為 CommonJS 模組時,就會將預設值放到 module.exports.default 上,概念上會長這樣。
export default const foo = 'bar'
// 轉換為 CommonJS =>
exports.__esModule = true;
exports.default = foo = 'bar';
但就我們目前的例子,使用 ES6 匯入 CommonJS,因為 CommonJS 不需要經過轉換,也就沒有 __esModule,所以 __webpack_require__.n 會直接回傳 module.exports 物件。
不過這就帶出了一個問題,為什麼 Webpack 還需要多呼叫一次 __webpack_require__.n?,這是因為無法確定當前匯入的 CommonJS 模組,是不是經過其他函式庫(ex. Babel)轉換過的結果,__esModule 就是一個約定,可以判斷這件事。
__esModule在許多轉換模組的函式庫都有實作,如: Babel, TypeScript, SystemJS。 可以參考以下的討論串,暸解 JavaScript 社群中的大大們,如何考慮 CommonJS 轉換到 ES2015 模組的各個面向,並引入__esModule約定。
CommonJS 載入 ES2015
編譯前: index.js, es6-module.js
編譯後:
/* 0 */
/* 編譯後的 index.js */
/***/ (function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) {
const es6Module = __webpack_require__(1)
console.log(es6Module.name)
es6Module.default()
/***/ }),
/* 1 */
/* 編譯後的 es6-module */
/***/ (function(module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
Object.defineProperty(__webpack_exports__, "__esModule", { value: true });
// Named export
const name = 'es6-module.js'
/* harmony export (immutable) */ __webpack_exports__["name"] = name;
// Default export
/* harmony default export */ __webpack_exports__["default"] = (function () {
console.log('This is ' + name + ' with ES6(harmony) export syntax')
});
/***/ })
如同上一段所說,ES2015 的模組經過 Webpack 處理後,會改變預設值的取用方式。
可以看到 CommonJS 模組取用 ES2015 模組預設值是用 es6Module.default(),而 ES2015 模組在輸出時,就已經是以 __webpack_exports__["default"] 輸出。